Lyme disease is a serious health issue that affects both humans and animals. It is caused by a bacterium called Borrelia burgdorferi, which is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick. While it is prevalent in certain parts of the world, it is particularly prevalent in North America.

1. What is Lyme Disease in Dogs?
Lyme disease in dogs is a bacterial infection caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium. This bacterium is transmitted through the bite of an infected tick, primarily the black-legged or deer tick. Dogs can become infected with Lyme disease when an infected tick attaches to their skin and begins to feed on their blood. The tick will then transmit the bacterium into the dog’s bloodstream, where it can then spread throughout the dog’s body.
2. Symptoms of Lyme Disease in Dogs
The symptoms of Lyme disease in dogs can vary from mild to severe. Some common symptoms of Lyme disease in dogs include:
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Joint pain and stiffness
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Lameness
In some cases, dogs may also experience more severe symptoms, such as kidney failure, heart disease, and even death.
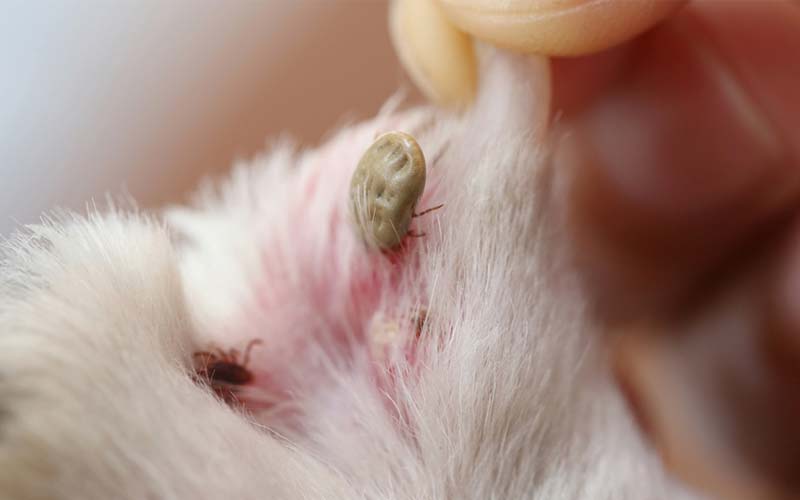
3. Diagnosing Lyme Disease in Dogs
Diagnosing Lyme disease in dogs can be challenging, as the symptoms can often be confused with other health issues. Your veterinarian will typically perform a blood test to detect the presence of the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium. This test will help your veterinarian to determine if your dog has been infected with Lyme disease.
4. Treating Lyme Disease in Dogs
Treatment for Lyme disease in dogs typically involves a course of antibiotics. The type of antibiotic used will depend on the severity of the infection and the overall health of the dog. In some cases, additional medications may be needed to help manage the symptoms of Lyme disease.
5. Preventing Lyme Disease in Dogs
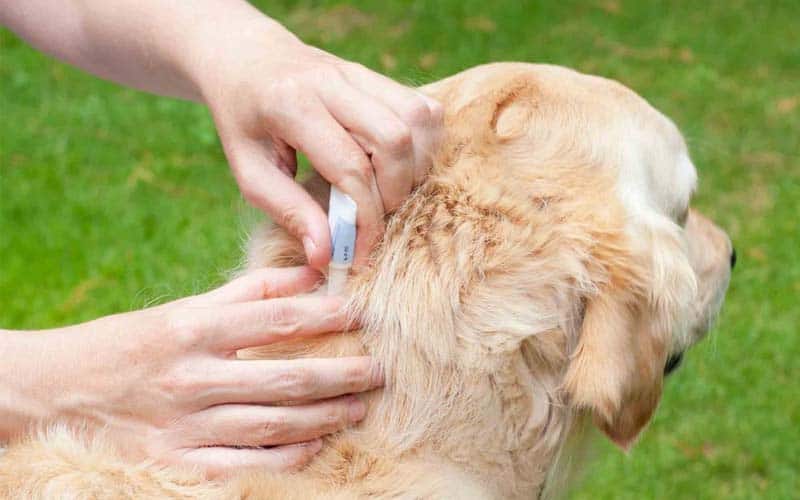
Preventing Lyme disease in dogs involves taking steps to reduce the risk of exposure to infected ticks. Some preventative measures pet owners can take include:
- Keeping dogs on a leash when outside
- Checking dogs for ticks regularly and removing them immediately
- Using tick preventative products, such as collars or topical treatments
- Avoiding areas where ticks are prevalent, such as wooded areas or tall grass
Conclusion
Lyme disease is a serious health issue that can affect both humans and animals. Pet owners should take steps to reduce the risk of exposure to infected ticks and seek treatment promptly if their dog is displaying any symptoms of Lyme disease. By working with their veterinarian, pet owners can help protect their furry friends from this potentially deadly disease.